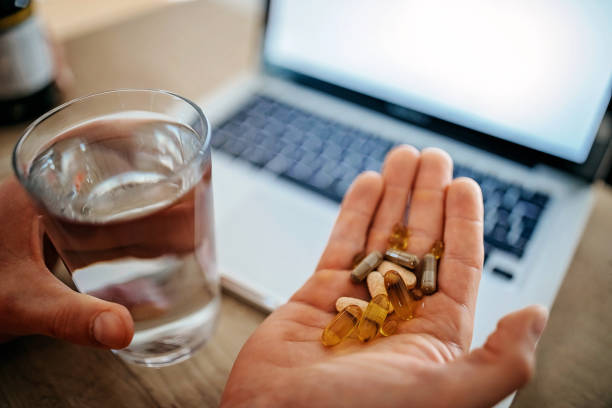
Free radicals are widely believed to contribute to aging and increase the risk of aging-related diseases like cancer and heart disease.1 The use of an antioxidant supplement is thought to neutralize free radicals, reducing or preventing cellular damage as well as the risk of certain diseases.
CoQ10 in supplement form is purported to improve heart-related conditions like hypertension (high blood pressure) by neutralizing free radicals, increasing the production of energy in cells, and preventing the formation of blood clots.2
It's important to know that CoQ10 is not an accepted or recommended medication for lowering blood pressure as outlined by national guidelines (ACC/AHA). And it should never be started as a remedy for high blood pressure without first consulting with a physician.
Hypertension Benefits
Among the cardiovascular conditions that may be prevented or treated with CoQ10 supplements are heart failure, heart attacks, and high blood pressure. For its part, the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database has rated CoQ10 as “possibly effective” for the treatment of hypertension.3
Some experts believe people with hypertension may have low concentrations of CoQ10 in their bodies. Several studies have suggested that CoQ10 can effect positive changes in blood pressure, generally within four to 12 weeks of use.4
Possible Side Effects
No major side effects have been reported with CoQ10 use, although some users have reported an upset stomach.5
Since studies have not determined safety during pregnancy, CoQ10 supplements are not recommended for use by pregnant women. People with diabetes should consult their healthcare professional before using CoQ10 supplements as the supplements may lower blood sugar.5
People who take blood thinners like Coumadin (warfarin) and Plavix (clopidogrel) should also speak with their healthcare professional before taking CoQ10 supplements, as the concomitant use of the drugs may increase the risk of bleeding and easy bruising.5
On the other hand, a number of small studies have suggested that CoQ10 may reduce cardiac toxicity associated with daunorubicin and doxorubicin, two chemotherapy drugs that are associated with heart muscle damage.6
Some medications can also lower the concentration of CoQ10 levels in your blood.
These include:
- Statin drugs like Crestor (rosuvastatin)
- Fibrates like Lopid (gemfibrozil)
- Tricyclic antidepressants like Elavil (amitryptiline) and Tofranil (imipramine)5
Dosage and Preparation
If you are on treatment for hypertension, the addition of CoQ10 supplements may allow you to decrease the dosage of other antihypertensive drugs. With that said, there is no guarantee that they will, and you should never change doses unless your doctor gives you the OK. Regular monitoring of blood pressure is needed before any such judgments can be made.
COQ10 should only be taken by adults 19 and older. Recommended dosages range from 30 mg to 200 mg daily, depending on the manufacturer. Soft gel capsules are thought to be absorbed better than other formulations.
What to Look For
It is important to note that supplements are not stringently regulated in the United States and that the quality can vary from one manufacturer to the next.
To ensure quality and safety, opt for brands that have been voluntarily submitted for testing by a third-party certifying authority like U.S. Pharmacopeia (USP), NSF International, or Consumer Lab. Certification ensures that the products on the ingredients label are listed.
Summary
If you have hypertension, supplements may or may not be useful in reducing your blood pressure. Research is lacking, and it's too soon to suggest that CoQ10 or is any other supplement is anywhere near as effective as proven strategies like routine exercise, improved diet, and smoking cessation.
If you are considering the use of a supplement like CoQ10, tell your healthcare professional. Some supplements may interact with the antihypertensive medications you take. It is also important to monitor your blood pressure regularly when making any changes in your treatment plan.